Glossary of terms in digital marketing and search engine optimization (SEO)
Based on generally accepted definitions as defined by Google as of September 2018.
Web presence - Any web page, whether owned by you or not, that mentions your brand and can show up as a search result listing. Your website certainly should be the most prominent part of your web presence, but other pages can show up as well, such as social media accounts, reviews from sites like Yelp or Google or Manta, externally published articles, videos on YouTube, mentions of your brand on other sites, and more. The bigger your web presence, the more you can dominate search results listings for search queries that relate to your brand.
Search engine - A software program that searches throughout a database of information to identify keywords or phrases specific by the user. Google is the largest and most popular search engine for online searches, followed closely by Yahoo! and Bing. Social media search engines also get a lot of press, such as that of YouTube, Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Algorithm - A process, set of rules, or program for the purpose of calculating various operations. In the context of SEO, the algorithms used by search engines determine which pages to suggest for a given search query.
Algorithm Update [Google] - Google is known for continually perfecting it’s search engine algorithm in order to deliver the most fitting, relevant results to the searcher. The more Google learns about natural language, searcher intent, and trends in content and web development, the more it fine-tunes its algorithm. If you keep up with digital marketing news, you may have heard of Google’s recent major algorithm updates, such as “Hummingbird,” “Panda,” “Pigeon,” etc.
Above the fold - Adapted from the newspaper term for the front-page area above the paper’s fold, this refers to the upper area of a website that appears on screen before the user has to scroll. It’s important to put the necessary introductory information above the fold so new visitors don’t have to scroll to figure out how to navigate the site. However, putting too much content above the fold can be distracting—the eye doesn’t know what to look at first.
Alt text/Alt Attributes - Text applied to images on a website, within the image’s HTML code, to explain what a picture/image placed on your site is about. This allows Google to index it, and it also helps blind users know what photos are on your site, via screen readers.
Analytics - Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from your website. Typically, this refers to Google Analytics, though some content management systems have their own analytics software that can provide similar data.
Anchor text - The clickable word(s) of an active hyperlink.
Anchor point - A point/location on a webpage, such as halfway down through the content or the very end, that a user can “jump” to based on a specially-coded link.
Authority (online credibility) - The combination of cues search engines use to determine websites and webpages’ credibility, which affects ranking.
Backlink (inbound link) - A link to a webpage or website that originates from an external website.
“Black hat” - Risky SEO techniques that go against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Most black hat methods were in attempt to “cheat the system” of Google’s algorithms, so Google made updates to penalize this type of activity that impeded user experience.
Blog - A blog is a website or page that is consistently updated with new information about a chosen topic. Often run by a single person or a small group of people, the writing tends to be less formal and more like a conversation.
Internet Bot - a software application that does an automated task over the internet. These tasks are usually simple and repetitive, and performed much faster than any human could. Bots are used for crawling the web to analyze and file information from web servers. The most common is referred to as a Spider, which are used by search engines to understand and categorize content.
Broken Link - A link that leads to a 404 Not Found error code. Generally, a link becomes broken when the destination URL is changed without arranging a redirect, when a website goes offline, or a web page is removed without implementing a redirect.
Bounce Rate - Percentage of visitors who leave without visiting another page on that website.
CMS (Content Management System) - This could refer to two types of software that create and manage digital content, often in a collaborative environment: web content management (WCM) and enterprise content management (ECM). WCM can refer to a web development platform such as WordPress, Joomla, Wix, Drupal, AdventistChurchConnect, Squarespace, etc.; ECM means a system of managing content alone, separate from the web development platform, but used in conjunction, and with extended content-focuses features such as content scheduling and collaborative editing.
Content - any information you place on your website. Content can be anything from written information, to infographics, to charts, to photos.
Content Marketing - Is the practice of creating content that is intended for a specific audience and optimizing that content to make it more easily found in search engines.
Conversion - When a user/visitor completes a desired action on a website.
Call to Action (CTA) - is the primary “ask” on a webpage—the action you want your reader to do after reading the convincing content on your page. For example, “Register for Webinar” or “Watch video now” or “Join today!” or “Donate now!” or “Download PDF.” It could also be, “Will you join our cause by supporting our goal financially?”
Clickbait - Content, primarily headlines, created to attract people to click. Often overly-dramatic, playing on emotions, oversimplifying, communicating urgency, and suspected of overpromising for the sake of getting more traffic, more reads, more sales, more sign-ups, etc.. Google’s most recent update further scrutinizes clickbait headlines to protect against misleading content. However, clickbait content done carefully and correctly can still make a big impact.
Crawl / Crawler / Spider- An internet “bot” that systematically categorizes and indexes websites and webpages to make sure they are categorized and listed appropriately.
Crawl Error - When a googlebot is blocked from crawling your website or web page. A page that is not crawled by googlebots will not be indexed and therefore cannot be found on the web.
Directory - Phonebooks of the internet. A directory lists the location of your organization, hours of operation, brief description, phone number, and photos. This helps significantly with local SEO, as each directory listing can show up as a separate search result. (It is extremely important that all information in your directory listings match exactly. See entry for “NAP.”)
Domain Name - The part of a website’s URL that directs your browser to the web server where a particular website is stored. In “analytics.google.com,” the domain name is “google.com.”
Duplicate Content - Blocks of content on a webpage that match content that exists elsewhere on the same website or a different website. It is possible for duplicate content to cause one page to rank in search results while the other will not, as Google indexes it as covering the same content. Quoting or referencing content is safe, but copied content is not. (Beware of tactics to “spin” content to make it only slightly different.)
Engagement - is the interaction between a visitor and your website. Did they click on a link, does it seem like they have read whole pages of your website all of these actions are used together to determine your websites engagement. A website with high engagement will do better than one with low or no engagement.
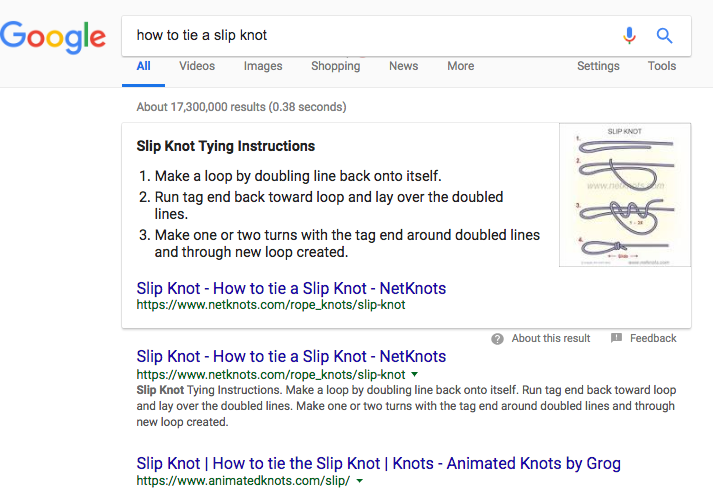
Featured Snippets - Found at the top of search results pages for certain topics, these are short captions that answers a commonly-asked question. Each snippet is extracted from a webpage the googlebot thinks best addresses the topic in a concise way. (example: google a topic like “how to tie a slip knot” and note the featured box on the top of the page)
Web presence - Any web page, whether owned by you or not, that mentions your brand and can show up as a search result listing. Your website certainly should be the most prominent part of your web presence, but other pages can show up as well, such as social media accounts, reviews from sites like Yelp or Google or Manta, externally published articles, videos on YouTube, mentions of your brand on other sites, and more. The bigger your web presence, the more you can dominate search results listings for search queries that relate to your brand.
Search engine - A software program that searches throughout a database of information to identify keywords or phrases specific by the user. Google is the largest and most popular search engine for online searches, followed closely by Yahoo! and Bing. Social media search engines also get a lot of press, such as that of YouTube, Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn.
Algorithm - A process, set of rules, or program for the purpose of calculating various operations. In the context of SEO, the algorithms used by search engines determine which pages to suggest for a given search query.
Algorithm Update [Google] - Google is known for continually perfecting it’s search engine algorithm in order to deliver the most fitting, relevant results to the searcher. The more Google learns about natural language, searcher intent, and trends in content and web development, the more it fine-tunes its algorithm. If you keep up with digital marketing news, you may have heard of Google’s recent major algorithm updates, such as “Hummingbird,” “Panda,” “Pigeon,” etc.
Above the fold - Adapted from the newspaper term for the front-page area above the paper’s fold, this refers to the upper area of a website that appears on screen before the user has to scroll. It’s important to put the necessary introductory information above the fold so new visitors don’t have to scroll to figure out how to navigate the site. However, putting too much content above the fold can be distracting—the eye doesn’t know what to look at first.
Alt text/Alt Attributes - Text applied to images on a website, within the image’s HTML code, to explain what a picture/image placed on your site is about. This allows Google to index it, and it also helps blind users know what photos are on your site, via screen readers.
Analytics - Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from your website. Typically, this refers to Google Analytics, though some content management systems have their own analytics software that can provide similar data.
Anchor text - The clickable word(s) of an active hyperlink.
Anchor point - A point/location on a webpage, such as halfway down through the content or the very end, that a user can “jump” to based on a specially-coded link.
Authority (online credibility) - The combination of cues search engines use to determine websites and webpages’ credibility, which affects ranking.
Backlink (inbound link) - A link to a webpage or website that originates from an external website.
“Black hat” - Risky SEO techniques that go against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Most black hat methods were in attempt to “cheat the system” of Google’s algorithms, so Google made updates to penalize this type of activity that impeded user experience.
Blog - A blog is a website or page that is consistently updated with new information about a chosen topic. Often run by a single person or a small group of people, the writing tends to be less formal and more like a conversation.
Internet Bot - a software application that does an automated task over the internet. These tasks are usually simple and repetitive, and performed much faster than any human could. Bots are used for crawling the web to analyze and file information from web servers. The most common is referred to as a Spider, which are used by search engines to understand and categorize content.
Broken Link - A link that leads to a 404 Not Found error code. Generally, a link becomes broken when the destination URL is changed without arranging a redirect, when a website goes offline, or a web page is removed without implementing a redirect.
Bounce Rate - Percentage of visitors who leave without visiting another page on that website.
CMS (Content Management System) - This could refer to two types of software that create and manage digital content, often in a collaborative environment: web content management (WCM) and enterprise content management (ECM). WCM can refer to a web development platform such as WordPress, Joomla, Wix, Drupal, AdventistChurchConnect, Squarespace, etc.; ECM means a system of managing content alone, separate from the web development platform, but used in conjunction, and with extended content-focuses features such as content scheduling and collaborative editing.
Content - any information you place on your website. Content can be anything from written information, to infographics, to charts, to photos.
Content Marketing - Is the practice of creating content that is intended for a specific audience and optimizing that content to make it more easily found in search engines.
Conversion - When a user/visitor completes a desired action on a website.
Call to Action (CTA) - is the primary “ask” on a webpage—the action you want your reader to do after reading the convincing content on your page. For example, “Register for Webinar” or “Watch video now” or “Join today!” or “Donate now!” or “Download PDF.” It could also be, “Will you join our cause by supporting our goal financially?”
Clickbait - Content, primarily headlines, created to attract people to click. Often overly-dramatic, playing on emotions, oversimplifying, communicating urgency, and suspected of overpromising for the sake of getting more traffic, more reads, more sales, more sign-ups, etc.. Google’s most recent update further scrutinizes clickbait headlines to protect against misleading content. However, clickbait content done carefully and correctly can still make a big impact.
Crawl / Crawler / Spider- An internet “bot” that systematically categorizes and indexes websites and webpages to make sure they are categorized and listed appropriately.
Crawl Error - When a googlebot is blocked from crawling your website or web page. A page that is not crawled by googlebots will not be indexed and therefore cannot be found on the web.
Directory - Phonebooks of the internet. A directory lists the location of your organization, hours of operation, brief description, phone number, and photos. This helps significantly with local SEO, as each directory listing can show up as a separate search result. (It is extremely important that all information in your directory listings match exactly. See entry for “NAP.”)
Domain Name - The part of a website’s URL that directs your browser to the web server where a particular website is stored. In “analytics.google.com,” the domain name is “google.com.”
Duplicate Content - Blocks of content on a webpage that match content that exists elsewhere on the same website or a different website. It is possible for duplicate content to cause one page to rank in search results while the other will not, as Google indexes it as covering the same content. Quoting or referencing content is safe, but copied content is not. (Beware of tactics to “spin” content to make it only slightly different.)
Engagement - is the interaction between a visitor and your website. Did they click on a link, does it seem like they have read whole pages of your website all of these actions are used together to determine your websites engagement. A website with high engagement will do better than one with low or no engagement.
Featured Snippets - Found at the top of search results pages for certain topics, these are short captions that answers a commonly-asked question. Each snippet is extracted from a webpage the googlebot thinks best addresses the topic in a concise way. (example: google a topic like “how to tie a slip knot” and note the featured box on the top of the page)
“Findability” - How easily the content on a website can be found, both by users and search engines.
Google Webmaster Guidelines - Google’s guidelines on acceptable website optimization practices, as well as improper practices that can result in manual action.
Google Analytics - A free web analytics program that can be used to contain performance, track audience behavior, traffic, content performance, and loads more.
Google Search Console - According to Google’s Search Console, it is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor and maintain your site's presence in Google Search results.
Footer - The footer is the information found at the bottom of a web page. Here you should place information such as your privacy policy, contact information, copyright, site map, Terms of use, Social Media Icons, email signup, Login information etc.
Footer Menu - is the information placed inside the footer, such as Navigation.
Header - The top of a webpage that typically displays a page title, navigation menu, hero image, or other introductory content.
Heading(s) - In web development and in word processing, headings can refer to styles such as H1, H2, H3…, which indicate the content hierarchy. There should only be one H1 per page, and best practices recommend they include the webpage’s keyword and entice the visitor to read the page.
Homepage - The default, or introductory web page, of a website.
Hero Image- Is a large image at the top of the page that takes up much of the screen when you enter a website. Sometimes they have text overlay, sometimes they
HTML / CSS - HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language used by web developers and is the standardized system that tags files so your site has the font, colors, graphics and hyperlink effects you want. CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets, or files dedicated to telling browsers how a page should be displayed, including various HTML elements. It is considered more efficient than using HTML alone, which can be repetitive.
HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol is how data is transferred from a computer server to a web browser.
HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure uses a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data transferred between a website and web browser. Google prefers to rank secure websites, so those that display https instead of http may perform better in search results.
Inbound Link - A link coming from another site to your own website. Also referred to as a backlink. When these are legitimate, they can demonstrate authority and credibility, which are ranking factors. If they are purchased or coerced, Google can penalize your site for having them.
Internal Link- a hyperlink from one page of your site to another page on your site. If your site is about cooking and you mention egg substitutes on one page, instead of explaining it on that page while you already have a page all about egg substitutes, you make the words “egg substitutes” into a hyperlink to the “All About Egg Substitutes” page on your site.
External Link - a link on your site that leads the user to another site. Best used for reference, citing sources, referrals to trusted sources, or as a way of avoiding reinventing the wheel if another site has information you’d like to include in your content progression. (Note: set external links to open in a new browser tab, so users don’t have to leave your page to view it.)
Index - The database search engines use to store and fetch information gathered during the “crawling” process.
Keywords - The words, phrases, topics, ideas, or questions that describe what your content is all about. This also refers to the words or phrases your target audience typically uses in Google searches. The goal is to match your audience’s language as much as possible, so Google sees your content as a good fit for their related searches.
Keyword Research - The process of discovering any relevant terms, topics, or subjects people enter into search engines. This can also include the rate of competition and the amount of searches conducted for each term or topic.
“Keyword Stuffing” - Repeating keywords beyond what is natural, in the hopes of increasing search rankings. This is now considered a spam tactic goes against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and can result in a ranking penalty.
Landing Page - A stand-alone web page designed to capture leads or generate conversions, usually with persuasive content built around a single, clear, concise call to action (sign up, download, subscribe, register, enter contest, etc.)
Manual Action - Google’s term for a penalty. According to Google, “The Manual Actions report lists instances where a human reviewer has determined that pages on your site are not compliant with Google's webmaster quality guidelines.” A penalized websites can either be demoted or removed from Google’s search results.
Metadata / Meta description - A description of a webpage’s content displayed under the webpage title in search results. While it isn’t used in ranking algorithms, it helps users preview the page content in the form of a teaser or intro, which can help convince them to click on that link.
Mobile Responsive / Mobile First - websites information like image, links, text, videos are easily shrunken and available across platforms like smartphones and tablets and still providing great user experience.
NAP - Internet acronym for “Name, Address and Phone Number,” used commonly in the subject of online directory listings, as it’s imperative that an organization’s NAP match exactly on each listing, or Google may count them as different/separate entities.
Navigation Menu / Website Navigation - A website’s main menu of links (Home, About, Contact, Services, Blog, etc.), telling the user what they can find on this website. It can also display the major topics the website covers.
Organic search results - What appears in search result listings after typing in a search query after paid ads or sponsored posts. “Organic” refers to the fact that the websites’ content is what caused them to rank, rather than pay-per-click advertising.
Page Speed - The amount of time it takes for a webpage to completely load. Page speed is ranking factor.
Paid search results - Pay-per-click advertisements that appear above and often below the organic results on search engines.
PPC (Pay-per-click) - A type of advertising where advertisers are charged a certain amount (usually determined by bid, relevance, account history, and competition) every time a user clicks on the ad.
Redirect - A technique that sends a user (or search engine) who requested one webpage to a different (but equally relevant) webpage.
There are two types of redirects:
Robots.txt - The Robots Exclusion Protocol (or Standard) is a text file, accessible at the root of a website, that tells search engine crawlers which areas of a website should be ignored.
ROI: Return on Investment. While a broadly used business term, ROI is often discussed in digital marketing and SEO because these practices are not cheap to apply, but can have remarkably positive effects on an organization’s online reputation, influence, and visibility.
RSS Feed - An acronym for Really Simple Syndication, RSS feeds allow content published on another site to display on your site. For example, daily news headlines, posts from a recommended blog, or even YouTube videos on a certain topic can be “fed” into a designated area on your website. You can also create content to be distributed via RSS to other websites.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) - to increase a website’s visibility in search engine results pages with both paid and organic activities.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) - The process of optimizing a website which includes the content, so it will appear in prominent positions in the organic search results of search engines like Google.
SERPs - Acronym for “Search Engine Results Page(s)”
Sitemap - A list of pages on a website. There are two types of sitemaps:
SSL Certificate (http vs https) - A digital certificate used for website identity authentication and to encrypt information sent to the server using Secure Sockets Layer technology.
Subdomain - A domain that is part of a primary domain: blog.thiswebsite.com.
Top Level Domain (TLD) - The extension of a given web address, such as .com, .org, .net, .info, etc.
Traffic - The measurement of people (and sometimes bots) who visit your website.
URL - The “physical” address of a web page. For example, https://www.sdadata.org/ and https://www.centerforonlineevangelism.org/ are URLs—it tells your browser which website to “go” to.
UX (User Experience) - The overall impressions users have while interacting with a brand, its online presence, and its product/services. Those who work in the field of User Experience Engineering (UXE) work as software or website reviewers/testers, as an advocate for users specifically in the digital field.
User-generated content (UGC) - Forms of content like blog posts, comments, podcasts, reviews, videos, blog posts, etc. that is created by customers or users about a certain brand.
Vlog - a blog in video form.
Webmaster - A person who manages the technical aspects of the website. Note: a webmaster is not the same as a web developer, though at times one person can occupy both roles. A webmaster may use a CMS to create, post, archive, or move content without getting into the code at all, while a developer has the capability to edit a website at the code level.
White Hat - Tactics that comply with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines (as opposed to “black hat”).
Widget - A stand-alone mini-program that can be installed/embedded into a website through code to perform a certain action. Widgets can be ads, submission forms, quizzes or polls, or they can display content from another website, such as headlines, weather, etc.
Webpage - A document that exists on the World Wide Web and can be viewed by web browsers. A website is made up of several webpages, linked together by a sitemap, or navigational structure.
Google Webmaster Guidelines - Google’s guidelines on acceptable website optimization practices, as well as improper practices that can result in manual action.
Google Analytics - A free web analytics program that can be used to contain performance, track audience behavior, traffic, content performance, and loads more.
Google Search Console - According to Google’s Search Console, it is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor and maintain your site's presence in Google Search results.
Footer - The footer is the information found at the bottom of a web page. Here you should place information such as your privacy policy, contact information, copyright, site map, Terms of use, Social Media Icons, email signup, Login information etc.
Footer Menu - is the information placed inside the footer, such as Navigation.
Header - The top of a webpage that typically displays a page title, navigation menu, hero image, or other introductory content.
Heading(s) - In web development and in word processing, headings can refer to styles such as H1, H2, H3…, which indicate the content hierarchy. There should only be one H1 per page, and best practices recommend they include the webpage’s keyword and entice the visitor to read the page.
Homepage - The default, or introductory web page, of a website.
Hero Image- Is a large image at the top of the page that takes up much of the screen when you enter a website. Sometimes they have text overlay, sometimes they
HTML / CSS - HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language used by web developers and is the standardized system that tags files so your site has the font, colors, graphics and hyperlink effects you want. CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets, or files dedicated to telling browsers how a page should be displayed, including various HTML elements. It is considered more efficient than using HTML alone, which can be repetitive.
HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol is how data is transferred from a computer server to a web browser.
HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure uses a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data transferred between a website and web browser. Google prefers to rank secure websites, so those that display https instead of http may perform better in search results.
Inbound Link - A link coming from another site to your own website. Also referred to as a backlink. When these are legitimate, they can demonstrate authority and credibility, which are ranking factors. If they are purchased or coerced, Google can penalize your site for having them.
Internal Link- a hyperlink from one page of your site to another page on your site. If your site is about cooking and you mention egg substitutes on one page, instead of explaining it on that page while you already have a page all about egg substitutes, you make the words “egg substitutes” into a hyperlink to the “All About Egg Substitutes” page on your site.
External Link - a link on your site that leads the user to another site. Best used for reference, citing sources, referrals to trusted sources, or as a way of avoiding reinventing the wheel if another site has information you’d like to include in your content progression. (Note: set external links to open in a new browser tab, so users don’t have to leave your page to view it.)
Index - The database search engines use to store and fetch information gathered during the “crawling” process.
Keywords - The words, phrases, topics, ideas, or questions that describe what your content is all about. This also refers to the words or phrases your target audience typically uses in Google searches. The goal is to match your audience’s language as much as possible, so Google sees your content as a good fit for their related searches.
Keyword Research - The process of discovering any relevant terms, topics, or subjects people enter into search engines. This can also include the rate of competition and the amount of searches conducted for each term or topic.
“Keyword Stuffing” - Repeating keywords beyond what is natural, in the hopes of increasing search rankings. This is now considered a spam tactic goes against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and can result in a ranking penalty.
Landing Page - A stand-alone web page designed to capture leads or generate conversions, usually with persuasive content built around a single, clear, concise call to action (sign up, download, subscribe, register, enter contest, etc.)
Manual Action - Google’s term for a penalty. According to Google, “The Manual Actions report lists instances where a human reviewer has determined that pages on your site are not compliant with Google's webmaster quality guidelines.” A penalized websites can either be demoted or removed from Google’s search results.
Metadata / Meta description - A description of a webpage’s content displayed under the webpage title in search results. While it isn’t used in ranking algorithms, it helps users preview the page content in the form of a teaser or intro, which can help convince them to click on that link.
Mobile Responsive / Mobile First - websites information like image, links, text, videos are easily shrunken and available across platforms like smartphones and tablets and still providing great user experience.
NAP - Internet acronym for “Name, Address and Phone Number,” used commonly in the subject of online directory listings, as it’s imperative that an organization’s NAP match exactly on each listing, or Google may count them as different/separate entities.
Navigation Menu / Website Navigation - A website’s main menu of links (Home, About, Contact, Services, Blog, etc.), telling the user what they can find on this website. It can also display the major topics the website covers.
Organic search results - What appears in search result listings after typing in a search query after paid ads or sponsored posts. “Organic” refers to the fact that the websites’ content is what caused them to rank, rather than pay-per-click advertising.
Page Speed - The amount of time it takes for a webpage to completely load. Page speed is ranking factor.
Paid search results - Pay-per-click advertisements that appear above and often below the organic results on search engines.
PPC (Pay-per-click) - A type of advertising where advertisers are charged a certain amount (usually determined by bid, relevance, account history, and competition) every time a user clicks on the ad.
Redirect - A technique that sends a user (or search engine) who requested one webpage to a different (but equally relevant) webpage.
There are two types of redirects:
- 301: Permanent
- 302: Temporary
Robots.txt - The Robots Exclusion Protocol (or Standard) is a text file, accessible at the root of a website, that tells search engine crawlers which areas of a website should be ignored.
ROI: Return on Investment. While a broadly used business term, ROI is often discussed in digital marketing and SEO because these practices are not cheap to apply, but can have remarkably positive effects on an organization’s online reputation, influence, and visibility.
RSS Feed - An acronym for Really Simple Syndication, RSS feeds allow content published on another site to display on your site. For example, daily news headlines, posts from a recommended blog, or even YouTube videos on a certain topic can be “fed” into a designated area on your website. You can also create content to be distributed via RSS to other websites.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) - to increase a website’s visibility in search engine results pages with both paid and organic activities.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) - The process of optimizing a website which includes the content, so it will appear in prominent positions in the organic search results of search engines like Google.
- Offsite SEO - Activities that are associated with your brand which take place outside of a website. Can include email marketing, social media marketing, TV, radio, high-quality natural backlinks, and more.
- Onsite SEO - Activities that take place directly on your website that help your pages rank. This includes SEO focuses such as title tags, meta tags, intuitive website navigation, intuitive sitemaps, high-quality content, etc.
SERPs - Acronym for “Search Engine Results Page(s)”
Sitemap - A list of pages on a website. There are two types of sitemaps:
- HTML: This type of sitemap, typically organized by topics, helps site users navigate a website.
- XML: This type of sitemap provides crawlers with a list of webpages on a website and assists the indexing process.
SSL Certificate (http vs https) - A digital certificate used for website identity authentication and to encrypt information sent to the server using Secure Sockets Layer technology.
Subdomain - A domain that is part of a primary domain: blog.thiswebsite.com.
Top Level Domain (TLD) - The extension of a given web address, such as .com, .org, .net, .info, etc.
Traffic - The measurement of people (and sometimes bots) who visit your website.
URL - The “physical” address of a web page. For example, https://www.sdadata.org/ and https://www.centerforonlineevangelism.org/ are URLs—it tells your browser which website to “go” to.
UX (User Experience) - The overall impressions users have while interacting with a brand, its online presence, and its product/services. Those who work in the field of User Experience Engineering (UXE) work as software or website reviewers/testers, as an advocate for users specifically in the digital field.
User-generated content (UGC) - Forms of content like blog posts, comments, podcasts, reviews, videos, blog posts, etc. that is created by customers or users about a certain brand.
Vlog - a blog in video form.
Webmaster - A person who manages the technical aspects of the website. Note: a webmaster is not the same as a web developer, though at times one person can occupy both roles. A webmaster may use a CMS to create, post, archive, or move content without getting into the code at all, while a developer has the capability to edit a website at the code level.
White Hat - Tactics that comply with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines (as opposed to “black hat”).
Widget - A stand-alone mini-program that can be installed/embedded into a website through code to perform a certain action. Widgets can be ads, submission forms, quizzes or polls, or they can display content from another website, such as headlines, weather, etc.
Webpage - A document that exists on the World Wide Web and can be viewed by web browsers. A website is made up of several webpages, linked together by a sitemap, or navigational structure.